- SQL (Structured Query Language) is a powerful programming language used for managing and manipulating relational databases. It allows users to create, retrieve, update, and delete data efficiently within a database system. SQL is widely used across industries for tasks ranging from data analysis to database management.
| 5 Method Of Introduction SQL |
| 1. Database |
| 2. Tables |
| 3. SQL Data Types |
| 4. Introducing Queries |
| 5. Writing Queries |
Table of Content
Relational Database
- A relational database is a type of database that organizes data into structured tables (relations) with rows and columns.
Database
purpose of introduction with SQL
- Understand databases and their structure
- Extract Information from databases using SQL

Patrons Table
| Column (field name) | Definition |
| card_num | card number |
| name | name |
| member_year | the year the patron became a library member. |
| total_fine | the total overdue |
Relational Database – -> relation between tables of data insider the database
Database Benefits
- Database have more storage than spreadsheet application.
- Many users can write queries to gather insights from the data at the same time.
Tables
Definition
- databases are organized into tables, which hold related data about a particular subject.
- tables are organized into rows and columns.
- in the world of databases, rows are often referred to as records and columns as fields.

book table and checkouts table connect with id column.
Create Table Name
- lowercase
- no space and – in table name (use underscores instead)
- plurals
Record and Field
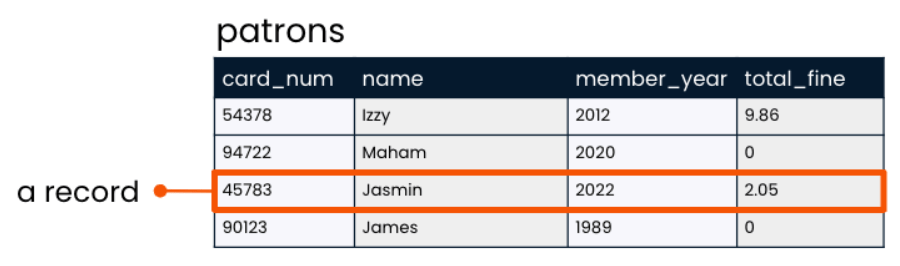
Records
- Laying the table : records
- A record is a row that holds data on an individual observation.
Fields
- Laying the table : fields
- A field is a column that holds one columns of data for all records.

Table manner
| Qualification |
| Singular name |
| No lowercase |
| No space |
| be different from other field name |
| be different from the table name |

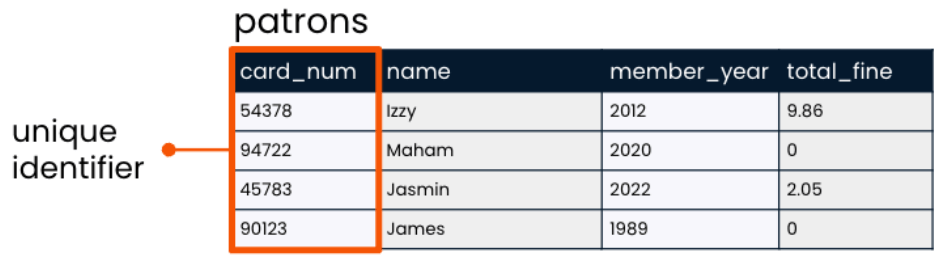
Assigned seats
- A unique identifier is used to identify records in a table.
- Distinct and often number.
Create books table
- A database has been set up for this course and the
bookstable is available here.
- Run the code to explore what data
booksholds!.
SELECT * FROM books;
SQL data types
- When a table is created, a data type must be indicated for each field. The data type is chosen based on the type of data that the field will hold a text and number.

| SQL Data type | Attribute |
| String | letters or punctuation |
| Integers | whole number |
| Floats | fractional number |
String
- String is a sequence of characters such as letters or punctuation.
- VARCHAR is a flexible and popular string data type in SQL.

Integers
- Integers is whole number
- INT is popular integer data type in SQL.

Floats
- Float store numbers that include a fractional part
- NUMERIC is popular float data type in SQL

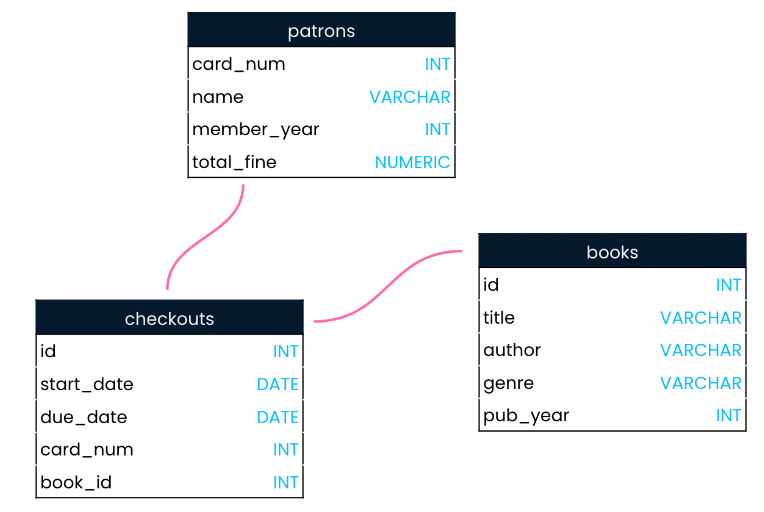
Schema
A schema shows a database’s design, such as what tables are included in the database and any relationships between its tables.
Querying
Introducing queries
Benefits of SQL
- use SQL to find which books James checked out from the library in 2022.

- use SQL queries to uncover trends in website traffic, customer reviews, and product sales.
| Question |
| Which products had the highest sales last week? |
| Which products get the worst review scores from customers? |
| How did website traffic change when a feature was introduced? |
Keyword
Keyword is word for operations. Common keywords : SELECT, FROM
- The SELECT keyword indicates which fields should be selected
- The FROM keyword indicates the table in which these fields are located
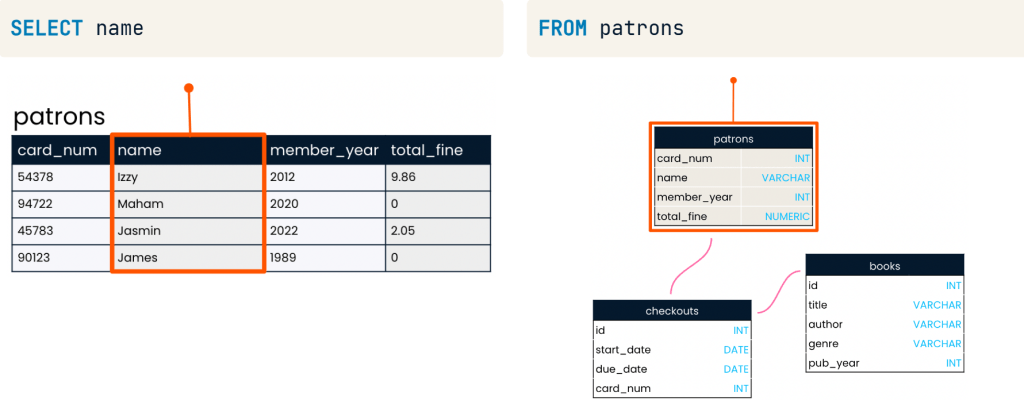
SELECT name FROM patrons;
Selecting multiple fields
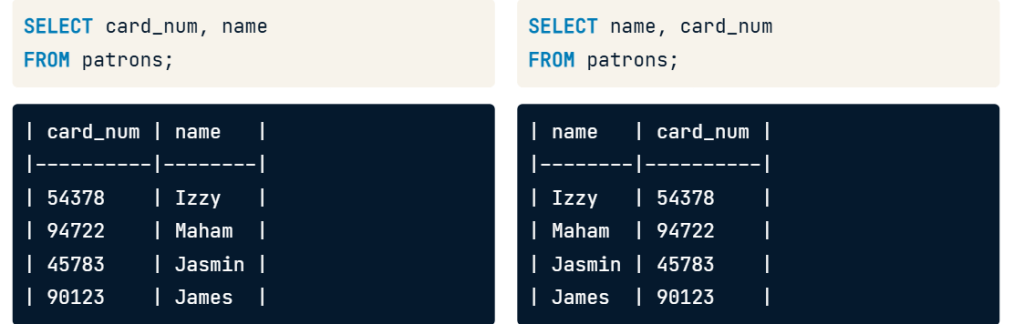
- Can select field to that want show data example card_num and name
SELECT card_num, name FROM patrons;
- It will show field that select first as picture below.
Selecting all fields
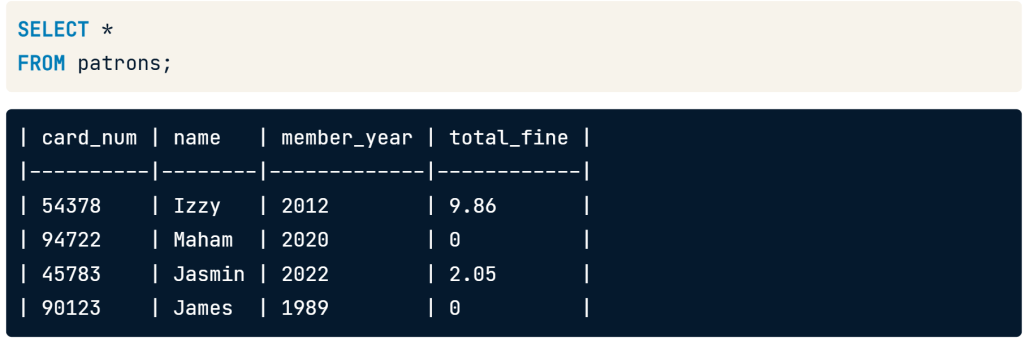
- if you want to show all data use asterisk(*) to select all four field name.
SELECT * FROM patrons;
Writing queries
Aliasing (Rename Column)
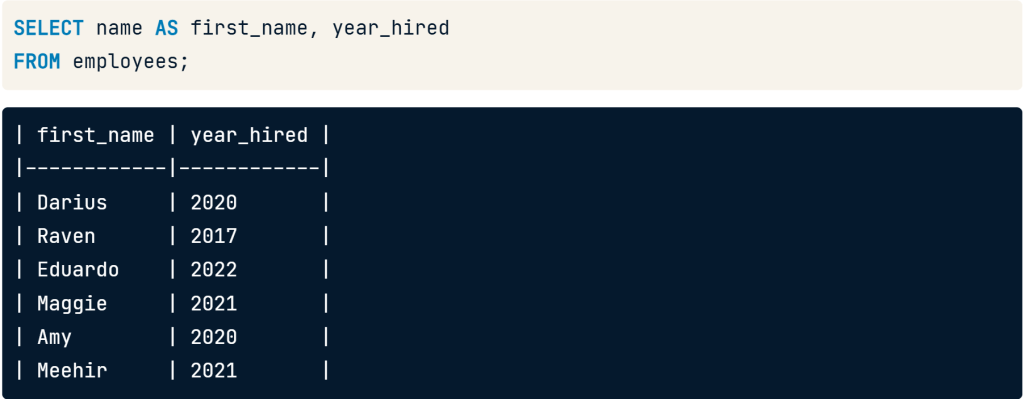
- Use aliasing to rename column.
Use SELECT name AS first_name to change field name from name to be first_name.
SELECT name AS first_name, year hired
FROM employees;
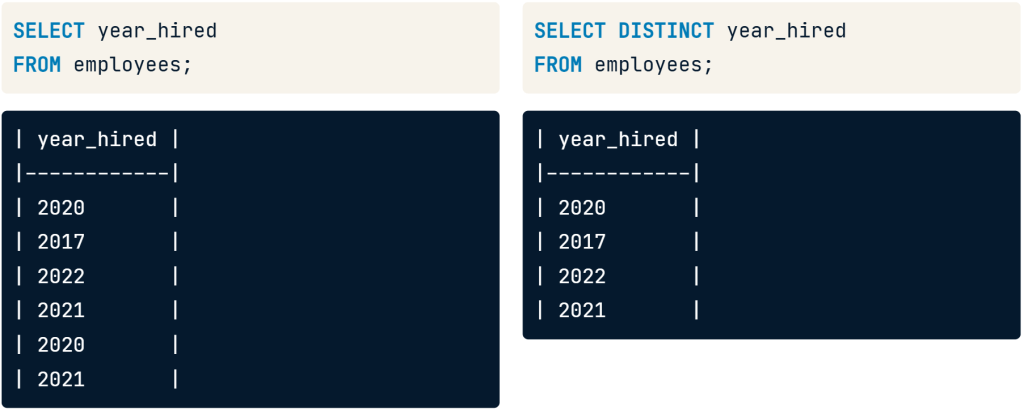
Selecting Distinct Records
- if you select year_hired it will show result duplicate year 2020 and 2021
- we can add the DISTINCT keyword before the year_hired that make data show 4 year distinct.
SELECT DISTINCT year_hired
FROM employees;
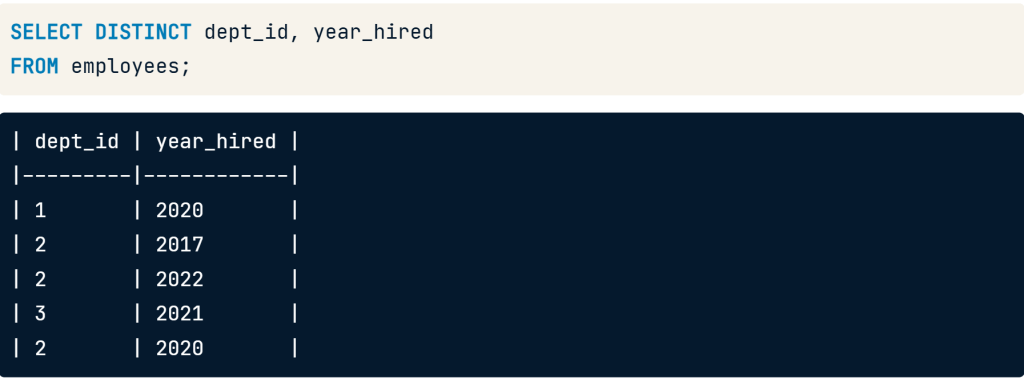
Distinct with multiple fields
- add the DISTINCT keyword before the fields to select
- the department id and year_hired fields still have repeat values individually, but none of the records are the same
SELECT DISTINCT dept_id, year_hired
FROM employees;
Views
- A view is a virtual table that save SQL SELECT statement
- When accessed, views automatically update in response to updates in the underlying data.
CREATE VIEW employee_hires_years AS
SELECT id, name, year_hired
FROM employees;
CREATE VIEW, then the name will create the new view.
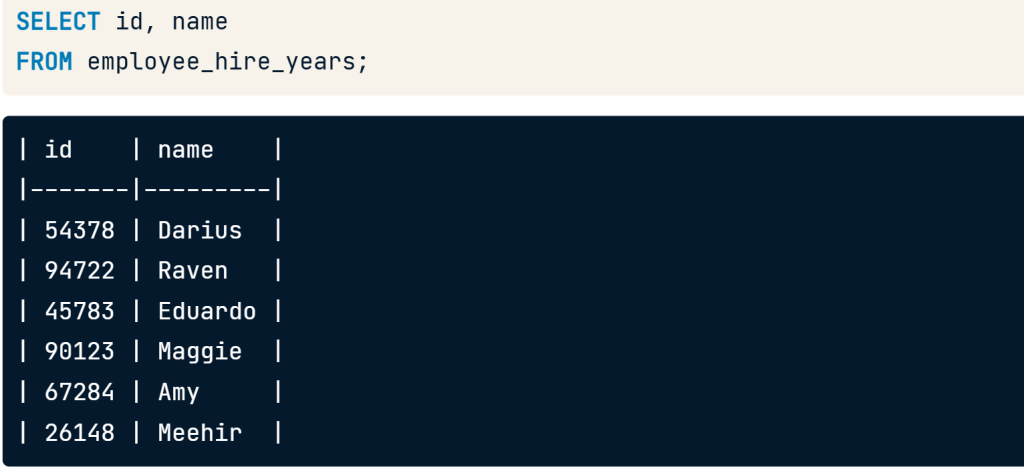
Using views
- we can query it just as we would a normal table by selecting FROM the view.
SELECT id, name
FROM employee_hire_years;
-- create the view:
CREATE VIEW library_authors AS
SELECT DISTINCT author AS unique_author
FROM books;
-- Select all columns from library_authors
SELECT * FROM library_authors

Viewing your query
- You have worked hard to create the below SQL query:
SELECT DISTINCT author AS unique_author
FROM books;
SQL flavors
- Both free and paid
- All used with relational database
- Vast majority of keywords are the same
- All must follow universal standards
Two popular SQL flavors
| PostgreSQL | SQL Server |
| Free and open-source relational database system. | Has free and paid version |
| Created at the university of California, Berkeley | Create by Microsoft |
| “PostgreSQL” refers to both the PostgreSQL database system and its associted SQL flavor | T-SQL is Microsoft SQL flavor, used with SQL Server databases |
Comparing PostgreSQL and SQL Server
--PostgreSQL:
SELECT id, name
FROM employees
LIMIT 2;
--SQL Server:
SELECT TOP(2) id, name
FROM employees;

SQL Server using the TOP keyword instead of LIMIT. Notice that this keyword is the only difference between the two queries!
Summary
“I hope the foundational knowledge for advancing projects in the following five areas will be helpful for everyone:
- Database
- Tables
- SQL Data Types
- Introducing Queries
- Writing Queries”
Introduction to SQL course

